In our previous discussion on “Porter’s Five Forces” framework, we gained insights into the various factors that shape market dynamics. Building upon that knowledge, let’s delve deeper into one crucial factor within the framework: the bargaining power of buyers. Buyers hold a pivotal position in any market, exerting significant influence over businesses and consumers alike. The concept of buyer bargaining power revolves around customers’ ability to impact product conditions, pricing, and terms. Recognizing and comprehending the extent of buyer bargaining power is indispensable for businesses aiming to devise effective strategies and maintain a competitive edge. In this article, we will closely examine the key factors that contribute to the bargaining power of buyers, unraveling its implications for both buyers and sellers in the process.
1. Definition of Bargaining Power of Buyers: The bargaining power of buyers, also known as customer power, represents the influence customers wield over businesses. It reflects the degree of control buyers have in a particular market and their ability to negotiate favorable terms, lower prices, or additional benefits.
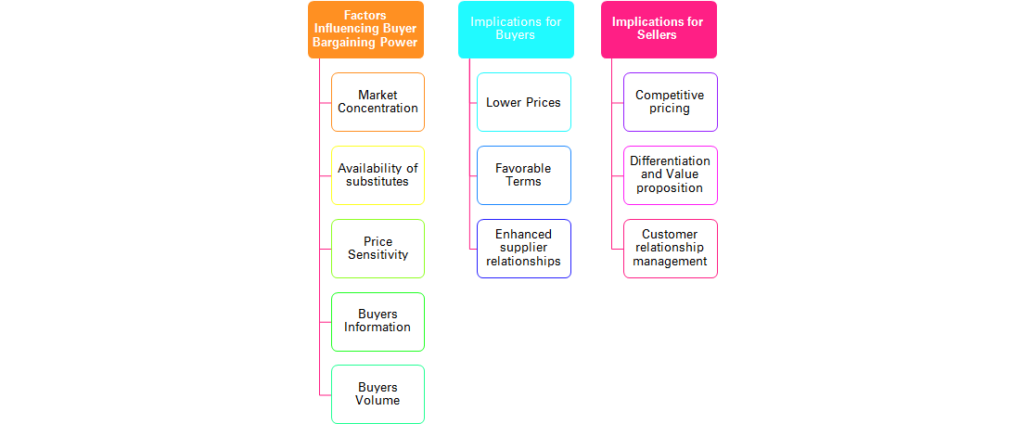
2. Factors Influencing Buyer Bargaining Power: Several factors impact the bargaining power of buyers. Understanding these factors helps businesses assess the level of buyer influence in their industry.
Some key factors include:
- Market Concentration: When buyers face limited options or a small number of dominant sellers, their bargaining power tends to increase. In contrast, a fragmented market with numerous suppliers may diminish buyer power.
- Availability of Substitutes: If buyers have access to alternative products or services that meet their needs, it strengthens their bargaining power. The more choices buyers have, the greater their ability to switch suppliers or negotiate better terms.
- Price Sensitivity: The price sensitivity of buyers affects their bargaining power. If buyers are highly price-sensitive or have low switching costs, they can demand lower prices or seek competitive offers.
- Buyer Information: The availability of information empowers buyers. With increased access to product details, reviews, and market comparisons, buyers can make more informed decisions and negotiate better deals.
- Buyer Volume: Larger buyers who make significant purchases have stronger bargaining power. The potential for bulk orders or long-term contracts provides leverage for negotiating lower prices or exclusive deals.
3. Implications for Buyers: Buyers with significant bargaining power enjoy several advantages:
- Lower Prices: Buyers can negotiate lower prices or secure discounts from suppliers, reducing their costs and increasing their profitability.
- Favorable Terms: Strong buyer power enables negotiating flexible payment terms, warranties, or after-sales services that benefit their business operations.
- Enhanced Supplier Relationships: Buyers with bargaining power can foster stronger relationships with suppliers, leading to preferential treatment, priority access to new products, or customized solutions
4. Implications for Sellers: Understanding buyer bargaining power is crucial for businesses to adapt their strategies:
- Competitive Pricing: Sellers need to analyze market dynamics and set competitive prices to attract buyers while maintaining profitability.
- Differentiation and Value Proposition: Offering unique products, superior quality, or exceptional customer service can help sellers mitigate buyer power by creating a perceived differentiation.
- Customer Relationship Management: Building strong relationships with buyers through personalized experiences and attentive customer support can strengthen loyalty and reduce the likelihood of buyer defection.
Conclusion: Recognizing and assessing the bargaining power of buyers is vital for businesses operating in any market. By understanding the factors that influence buyer power, both buyers and sellers can make informed decisions to navigate the market effectively. A balanced approach that considers the needs and preferences of buyers while maintaining profitability is key to achieving sustainable success in today’s competitive landscape.